NSG 6420 Week 4 Quiz
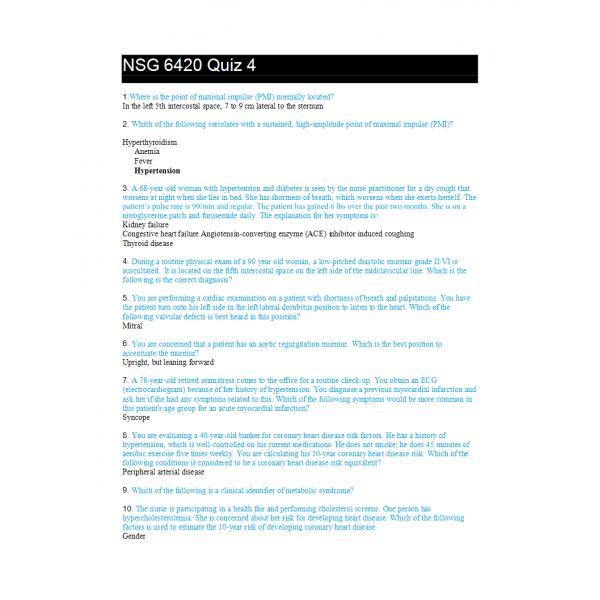
NSG 6420 Quiz 4
1.Where is the point of maximal impulse (PMI) normally located?
2.Which of the following correlates with a sustained, high-amplitude point of maximal impulse (PMI)?
3. A 68-year-old woman with hypertension and diabetes is seen by the nurse practitioner for a dry cough that worsens at night when she lies in bed. She has shortness of breath, which worsens when she exerts herself. The patient’s pulse rate is 90/min and regular. The patient has gained 6 lbs over the past two months. She is on a nitroglycerine patch and furosemide daily. The explanation for her symptoms is:
4.During a routine physical exam of a 90 year old woman, a low-pitched diastolic murmur grade II/VI is auscultated. It is located on the fifth intercostal space on the left side of the midclavicular line. Which is the following is the correct diagnosis?
5.You are performing a cardiac examination on a patient with shortness of breath and palpitations. You have the patient turn onto his left side in the left lateral decubitus position to listen to the heart. Which of the following valvular defects is best heard in this position?
6. You are concerned that a patient has an aortic regurgitation murmur. Which is the best position to accentuate the murmur?
Upright, but leaning forward
7. A 78-year-old retired seamstress comes to the office for a routine check-up. You obtain an ECG (electrocardiogram) because of her history of hypertension. You diagnose a previous myocardial infarction and ask her if she had any symptoms related to this. Which of the following symptoms would be more common in this patient's age group for an acute myocardial infarction?
8. You are evaluating a 40-year-old banker for coronary heart disease risk factors. He has a history of hypertension, which is well-controlled on his current medications. He does not smoke; he does 45 minutes of aerobic exercise five times weekly. You are calculating his 10-year coronary heart disease risk. Which of the following conditions is considered to be a coronary heart disease risk equivalent?
9. Which of the following is a clinical identifier of metabolic syndrome?
10. The nurse is participating in a health fair and performing cholesterol screens. One person has hypercholesterolemia. She is concerned about her risk for developing heart disease. Which of the following factors is used to estimate the 10-year risk of developing coronary heart disease
11. A 58-year-old teacher presents to your clinic with a complaint of breathlessness with activity. The patient has no chronic conditions and does not take any medications, herbs, or supplements. Which of the following symptoms is appropriate to ask about in the cardiovascular review of systems?
12. You notice a patient has a strong pulse and then a weak pulse. This pattern continues. Which of the following is likely?
13. cardiac tamponade
14.Radiological findings with severe left heart failure
15.You find a bounding carotid pulse on a 62-year-old patient. Which murmur should you search out?
16. During a routine physical exam of a 90-year-old woman, a low-pitched diastolic murmur Grade II/VI is auscultated. It is located on the fifth intercostal space on the left side of the midclavicular line. Which of the following is the correct diagnosis?
17.Grade II/VI is auscultated. It is located on the fifth intercostal space on the left side of the midclavicular line.
18. Mitral regurgitation
19. mitral stenosis
20. aortic regurtation
21. tricuspid regurgitation
22. waist size 38 in a male
23. BP 134/88 for a male
24. BP 128/84 in a female
25. You are screening people at the mall as part of a health fair. The first person who comes for screening has a blood pressure of 132/85. How would you categorize this
26. How should you determine whether a murmur is systolic or diastolic?
27. Where is the point of maximal impulse (PMI) normally located?Term
28.When listening to a soft murmur or bruit, which of the following may be necessary?
29. On examination, you find a bounding carotid pulse on a 62-year-old patient. Which murmur should you suspect?
30. Term
| Institution & Term/Date | |
| Term/Date | South University |
-
$12.00