MN 568 Unit 6 Quiz
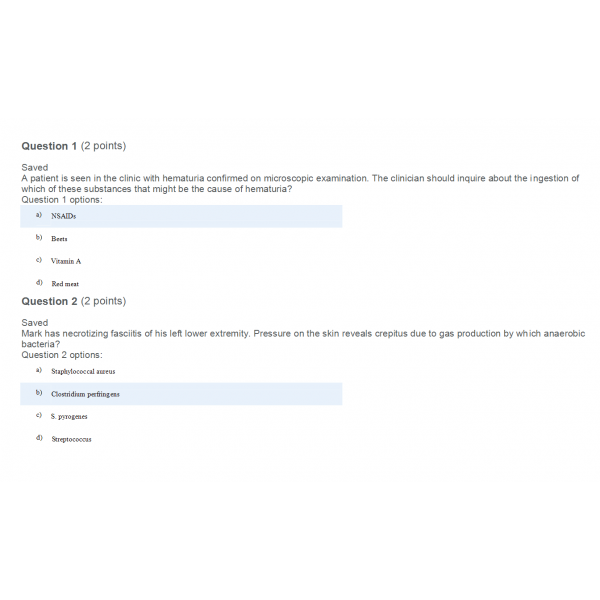
1. A patient is seen in the clinic with hematuria confirmed on microscopic examination. The clinician should inquire about the ingestion of which of these substances that might be the cause of hematuria?
2. Mark has necrotizing fasciitis of his left lower extremity. Pressure on the skin reveals crepitus due to gas production by which anaerobic bacteria?
3. Which of the following is “a linear crack extending from the epidermis to the dermis?”
4. The patient is diagnosed with ARF. Which of the following conditions is the most common cause?
5. A 14-year-old male is seen with complaints of severe testicular pain. The clinician suspects testicular torsion. Which of the following is the appropriate action?
6. Which scalp problem can be caused by a fever and certain drugs?
7. A 46-year-old man presents with urinary hesitancy and low back pain. He has no history of UTI. Digital rectal examination (DRE) reveals a normal prostate, and a diagnosis of prostatodynia is made. Which is the appropriate treatment?
8. The most common precancerous skin lesion found in Caucasians is:
9. A 27-year-old female presents with a chief complaint of burning and pain on urination. She has no previous history of urinary tract infection (UTI). What are some additional symptoms consistent with a diagnosis of lower UTI?
10. Which is the most potent and irritating dose of tretinoin?
11. Prevalence of psoriasis is highest in which group?
12. A patient is seen with a sudden onset of flank pain accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and diaphoresis. In addition to nephrolithiasis, which of the following should be added to the list of differential diagnoses?
13. Simon presents with alopecia areata with well-circumscribed patches of hair loss on the crown of his head. How do you respond when he asks you the cause?
14. Which of the following is an infraorbital fold skin manifestation in a patient with atopic dermatitis?
15. An example of ecchymosis is:
16. Harvey has a rubbery, smooth, round mass on his chest that is compressible and has a soft-to-very-firm texture. What do you diagnose this as?
17. When instructing your elderly client about treating her xerosis, what do you tell her?
18. A 23-year-old sexually active man is seen in the clinic with unilateral painful testicular swelling, and he is diagnosed with epididymitis. In order to prescribe the correct drug, the clinician must understand that which of these is the most common causative organism?
19. Which of the following instructions should be given to the patient with nephrolithiasis?
20. A 60-year-old man presents with an enlarged scrotum. The clinician uses a penlight to transilluminate the scrotum. In a patient with a hydrocele, what would the clinician expect to find?
21. Sally, age 25, presents with impetigo that has been diagnosed as infected with Staphylococcus. The clinical presentation is pruritic tender, red vesicles surrounded by erythema with a rash that is ulcerating. Her recent treatment has not been adequate. Which type of impetigo is this?
22. Why do people of African descent have a lower incidence of non-melanoma skin cancer?
23. The 56-year-old man with chronic prostatitis should be treated with trimethoprim 80 mg-sulfamethoxazole 400 mg (TMP-SMX, Bactrim) for how long?
24. Tinea unguium is also known as:
25. An 86-year-old woman is seen in the clinic for recurrent hematuria. The provider suspects bladder cancer. Which of the following data from the history is considered a risk factor for this type of cancer?
26. During a DRE on a 75-year-old man, the clinician suspects the patient has prostate cancer. What physical finding should make the clinician suspicious?
27. Josh, aged 22, has tinea versicolor. Which description is the most likely for this condition?
28. A patient is seen in the clinic and diagnosed with Stage I renal cancer. The provider should refer the patient to a nephrologist for which of these treatments?
29. A patient presents with CVA tenderness and a several-day history of high fever, chills, and dysuria. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely given the above information?
30. A 30-year-old patient presents with pain on urination. The urine microscopy of unspun urine shows greater than 10 leukocytes/mL, and a dipstick is positive for nitrites. What is the probable diagnosis?
31. When looking under the microscope to diagnose an intravaginal infection, you see a cluster of small and oval to round shapes. What do you suspect they are?
32. An example of a primary skin lesion is a/an:
33. A 63-year-old man is seen in the clinic with a chief complaint of nocturia. Which of the following should be included in the differential diagnosis?
34. A 76-year-old man is seen in the office for complaints of urinary incontinence. The clinician should explore which of these causes of incontinence in men?
35. A 42-year-old woman is seen in the clinic with fever, chills, vomiting, and severe dysuria. She is diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis. How should this patient be managed?
36. A 78-year-old man is diagnosed with C2 prostate cancer, and he asks the clinician what that means. In order to answer the patient, the clinician must have which of these understandings of the Jewett rating system?
37. The clinician should prescribe an antibiotic that covers which of these organisms for a patient with acute prostatitis?
38. A 34-year-old patient was treated for a UTI and has not responded to antibiotic therapy. Which of the following actions should be taken next?
39. Which of the following tests is most useful in determining renal function in a patient suspected of CRF?
40. The patient with BPH is seen for follow-up. He has been taking finasteride (Proscar) for 6 months. The clinician should assess this patient for which of these side effects?
41. Which of the following foods should be limited in a patient with CRF?
42. Of the following types of cellulitis, which is a streptococcal infection of the superficial layers of the skin that does not involve the subcutaneous layers?
43. Tori is on systemic antifungals for a bad tinea infection. You are aware that the antifungals may cause:
44. A bulla is:
45. Marci has a wart on her hand. She says she heard something about “silver duct tape therapy.” What do you tell her about his?
46. An 82-year-old woman with renal failure is seen in the clinic. The provider should question the patient about the intake of which of these substances that can cause renal toxicity?
47. A patient with testicular cancer is being followed after completing treatment 1 year ago. He has been symptom-free with no evidence of disease. How often should he have a CT scan?
48. Which of the following statements is accurate when you are removing a seborrheic keratosis lesion using liquid nitrogen?
49. A 35-year-old man presents with complaints of painful erections, and he notices his penis is crooked when erect. What is the most likely diagnosis?
50. Jeffrey has atopic dermatitis. You are prescribing a low-dose topical corticosteroid for him. Which would be a good choice?
| Institution & Term/Date | |
| Term/Date | Kaplan University |
MN 568 Unit 6 Quiz (Set 3)
- Product Code: 2022
- Availability: In Stock
-
$19.99
Related Products
MN 568 Unit 2 Quiz (Set 1)
$19.99
MN 568 Unit 2 Quiz (Set 2)
$19.99
MN 568 Unit 2 Quiz (Set 3)
$19.99
MN 568 Unit 4 Quiz (Set 2)
$19.99
MN 568 Unit 4 Quiz (Set 3)
$19.99
MN 568 Unit 6 Quiz (Set 1)
$19.99
MN 568 Unit 6 Quiz (Set 2)
$19.99
MN 568 Unit 8 Quiz (Set 1)
$19.99
MN 568 Unit 8 Quiz (Set 2)
$19.99
MN 568 Unit 8 Quiz (Set 3)
$19.99
MN 568 Unit 4 Quiz (Set 1)
$19.99









-200x200.JPG)
-200x200.JPG)