NSG 6435 Week 4 Quiz/ NSG6435 Week 4 Quiz: South University
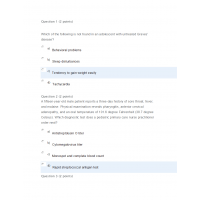
1. A school-age client presents to the clinic to establish care. The child has autism, facial dysmorphia, and growth retardation. The provider suspects the child has what condition?
2. A 8-year-old client was recently discharged from the hospital following an episode of meningitis. The client presented to the clinic for a follow-up appointment post discharge. The provider understands that the client’s is at increased risk for which complication(s)? (check all that apply)
3. A client with history of bilateral tympanostomy tube insertion presents to the clinic c/o otorrhea. The provider confirms the complaint. What is the best treatment for this condition? Question 4 The gold standard in diagnosing acute otitis media is:
4. A provider is caring for a new client whose had recurrent episodes of and failed treatment for acute otitis media. What is the next best intervention?
5. A 16 year-old-client presents to your clinic c/o sore throat and 101°F temperature. The provider learns that the client had a sore throat approximately 1 week ago. On exam, client is positive for cervical lymphadenopathy, enlarged left tonsil, edematous pharynx and uvula displacement. What condition does this client most likely have?
6. A 5-year-old client presents to the clinic for an annual physical. While performing the physical exam, the provider attempts to examine the client’s ears. What does the provider do?
7. What are the most common causes of bacterial pneumonia in neonates (select all that apply)?
8. An ill appearing 3-month-old-infant is presented to your clinic. The parent reports that their child has a fever, persistent cough, rhinorrhea, wheezing, hypoxemia, and anorexia for 4 days. After the provider’s exam and work-up, the child is diagnosed with Bronchiolitis. What is the most likely treatment option for this infant?
9. An ill-appearing child is presented to your clinic with a fever, sore throat, restless behavior, dysphagia, drooling, and inspiratory distress without stridor. The child tests positive for Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib). What is the most likely diagnosis?
| Institution & Term/Date | |
| Term/Date | South University |
NSG 6435 Week 4 Quiz 1
- Product Code: 2022
- Availability: In Stock
-
$9.99
Related Products
NSG 6435 Final Exam
$35.00
NSG 6435 Midterm Study Guide
$25.00
NSG 6435 Week 1 Quiz
$9.99
NSG 6435 Week 1 to 10 Quiz
$25.00
NSG 6435 Week 2 Quiz 1
$6.99
NSG 6435 Week 3 Quiz 1
$9.99
NSG 6435 Week 3 Quiz 2
$9.99
NSG 6435 Week 4 Quiz 2
$6.99
NSG 6435 Week 6 Quiz
$9.99
NSG 6435 Week 7 Quiz
$9.99
NSG 6435 Week 8 Quiz
$9.99
NSG 6435 Week 9 Quiz
$5.99